This example shows you how to connect to a WEP encrypted 802.11b/g network with the Arduino WiFi shield. Your Arduino Software (IDE) serial monitor will provide information about the connection once it has connected.
Arduino WiFi Shield
Shield-compatible Arduino board
The WiFi shield uses pins 10, 11, 12, and 13 for the SPI connection to the HDG104 module. Digital pin 4 is used to control the chip select pin on the SD card.
You should have access to a 802.11b/g wireless network that connects to the internet for this example. You will need to change the network settings in the sketch to correspond to your particular networks SSID.
WEP network passwords are hexadecimal strings known as keys. A WEP network can have 4 different keys; each key is assigned a "Key Index" value. For WEP encrypted networks, you need the SSID, the key, and key number.
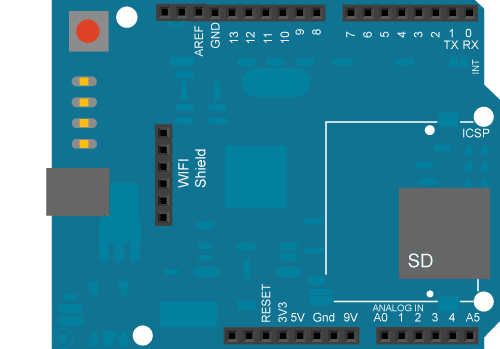
Image developed using Fritzing . For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
In the above image, the Arduino would be stacked below the WiFi shield.
/*H******************************************************* Connects to a WEP-encrypted Wifi network. Then it prints MAC address of Wifi shield, IP address obtained, and other network details. If you use 40-bit WEP, you need a key that is 10 characters long, and characters must be hexadecimal (0-9 or A-F). e.g. for 40-bit, ABBADEAF01 will work, but ABBADEAF won't work (too short) and ABBAISDEAF won't work (I and S are not hexadecimal characters). For 128-bit, you need a string that is 26 characters long. D0D0DEADF00DABBADEAFBEADED will work because it's 26 characters, all in the 0-9, A-F range. Circuit: * WiFi shield attached created 13 July 2010 by dlf (Metodo2 srl) ********************************************************/ #include#include //************************* DEFINES ************************************ //************************* PROTOTYPES ************************************ void printWifiData(); void printCurrentNet(); //************************* VARIABLES ************************************ char ssid[] = "yourNetwork"; // YOUR NETWORK SSID (NAME) char key[] = "D0D0DEADF00DABBADEAFBEADED"; // YOUR NETWORK KEY int keyIndex = 0; // YOUR NETWORK KEY INDEX NUMBEr int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS; // Wifi RADIO'S STATUS /*F******************************************************************** * **********************************************************************/ void setup() { Serial.begin( BAUD ); while( !Serial ) // INITIALIZE SERIAL AND WAIT FOR PORT TO OPEN { ; } // WAIT FOR SERIAL PORT TO CONNECT. NEEDED FOR NATIVE USB PORT ONLY if( WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SHIELD ) // CHECK FOR PRESENCE OF SHIELD { Serial.println( "WiFi shield not present"); while( true ); // don't continue: } String fv = WiFi.firmwareVersion(); if( fv != "1.1.0") Serial.println("Please upgrade firmware"); while( status != WL_CONNECTED ) // ATTEMPT TO CONNECT TO Wifi NETWORK { Serial.print( "Attempting to connect to WEP network, SSID: "); Serial.println( ssid ); status = WiFi.begin( ssid, keyIndex, key); delay( 10000 ); // wait 10 seconds for connection: } Serial.print("You're connected to the network"); printCurrentNet(); printWifiData(); // ONCE YOU ARE CONNECTED } /*F******************************************************************** * **********************************************************************/ void loop() { delay( 10000 ); // CHECK NETWORK CONNECTION ONCE EVERY 10 SECONDS printCurrentNet(); } /*F******************************************************************** * **********************************************************************/ void printWifiData() { IPAddress ip = WiFi.localIP(); Serial.print( "IP Address: "); // PRINT YOUR WiFi SHIELD'S IP ADDRESS Serial.println( ip ); Serial.println( ip ); byte mac[6]; WiFi.macAddress( mac ); Serial.print( "MAC address: " ); // print your MAC address: Serial.print( mac[5], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( mac[4], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( mac[3], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( mac[2], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( mac[1], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.println( mac[0], HEX ); } /*F******************************************************************** * **********************************************************************/ void printCurrentNet() { Serial.print( "SSID: " ); Serial.println( WiFi.SSID() ); // PRINT SSID OF NETWORK YOU'RE ATTACHED TO byte bssid[6]; WiFi.BSSID( bssid ); // PRINT MAC ADDR OF YOU'RE ROUTER Serial.print( "BSSID: " ); Serial.print( bssid[5], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( bssid[4], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( bssid[3], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( bssid[2], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.print( bssid[1], HEX ); Serial.print( ":" ); Serial.println( bssid[0], HEX ); long rssi = WiFi.RSSI(); Serial.print("signal strength (RSSI):"); // PRINT RECEIVED SIGNAL STRENGTH Serial.println( rssi ); byte encryption = WiFi.encryptionType(); Serial.print( "Encryption Type:" ); Serial.println( encryption, HEX ); // PRINT ENCRYPTION TYPE Serial.println(); }