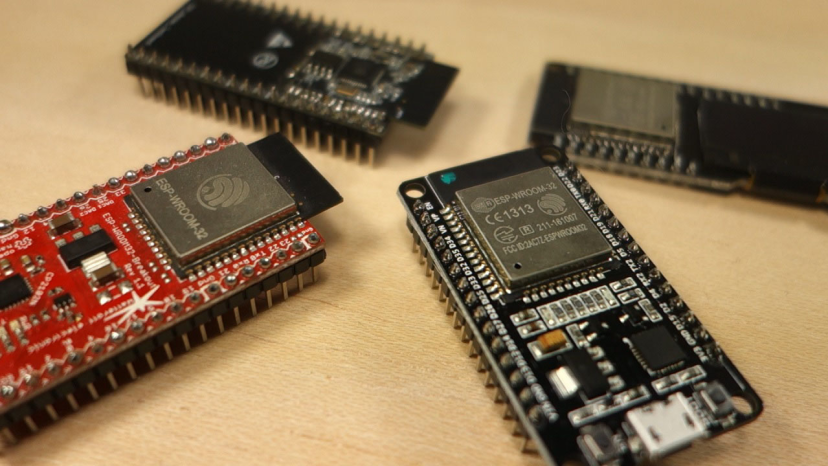
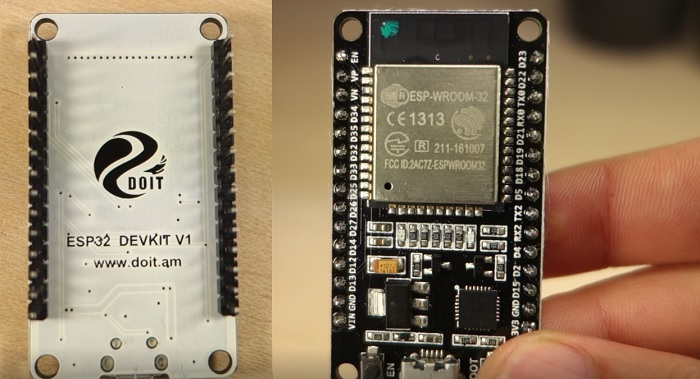
Specifications
When it comes to the ESP32 chip specifications, you’ll find that:
- The ESP32 is dual core, this means it has 2 processors.
- It has Wi-Fi and bluetooth built-in.
- It runs 32 bit programs.
- The clock frequency can go up to 240MHz and it has a 512 kB RAM.
- This particular board has 30 or 36 pins, 15 in each row.
- It also has wide variety of peripherals available, like: capacitive touch, ADCs, DACs, UART, SPI, I2C and much more.
- It comes with built-in hall effect sensor and built-in temperature sensor.
Specifications – ESP32 DEVKIT V1 DOIT
| Number of cores | 2 (dual core) |
| Wi-Fi | 2.4 GHz up to 150 Mbits/s |
| Bluetooth | BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) and legacy Bluetooth |
| Architecture | 32 bits |
| Clock frequency | Up to 240 MHz |
| RAM | 512 KB |
| Pins | 30 or 36 (depends on the model) |
| Peripherals | Capacitive touch, ADC (analog to digital converter), DAC (digital to analog converter), I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), UART (universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter), CAN 2.0 (Controller Area Netwokr), SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), I2S (Integrated Inter-IC Sound), RMII (Reduced Media-Independent Interface), PWM (pulse width modulation), and more. |
To learn more about the ESP32 GPIOs, read our GPIO reference guide: ESP32 Pinout Reference: Which GPIO pins should you use?
Programming Environments
The ESP32 can be programmed in different programming environments. You can use:
- Arduino IDE
- Espressif IDF (IoT Development Framework)
- Micropython
- JavaScript
- LUA
- …
In our projects, we program the ESP32 mainly with Arduino IDE or MicroPython
Preparing the ESP32 Board in Arduino IDE
There’s an add-on for the Arduino IDE allows you to program the ESP32 using the Arduino IDE and its programming language. Follow one of the next tutorials to prepare your Arduino IDE:
- Windows instructions – Installing the ESP32 Board in Arduino IDE
- Mac and Linux instructions – Installing the ESP32 Board in Arduino IDE
ESP32 Pinout Guide
The ESP32 has more GPIOs with more functionalities compared to the ESP826.
With the ESP32 you can decide which pins are UART, I2C, or SPI – you just need to set that on the code. This is possible due to the ESP32 chip’s multiplexing feature that allows to assign multiple functions to the same pin. If you don’t set them on the code, the pins will be used as default – as shown in the figure below (the pin location can change depending on the manufacturer).
Version with 30 Pin GPIOs
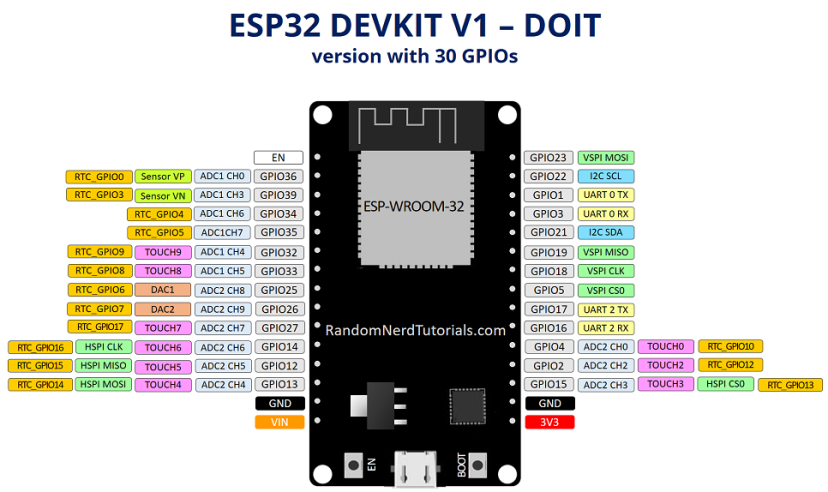
Version with 36 Pin GPIOs
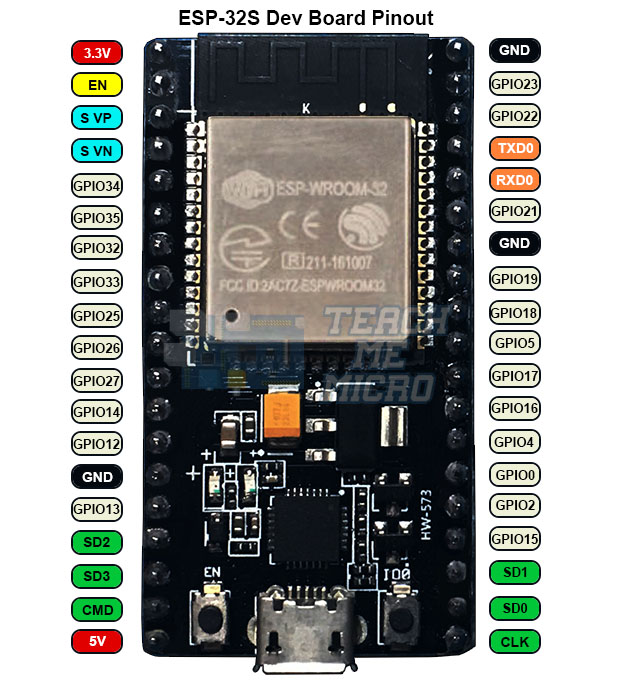
You can read our detailed ESP32 Pinout Reference Guide .
Upload Code to the ESP32 using Arduino IDE
To show you how to upload code to your ESP32 board, we’ll build a simple example to blink an LED.
Copy the following code to your Arduino IDE:
/*
Blink
*/
// ledPin refers to ESP32 GPIO 23
const
int ledPin
=
<23
;
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the boardvoid
setup
(
)
{
// initialize digital pin ledPin as an output.
pinMode
(ledPin
, OUTPUT
)
;
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forevervoid
loop
(
)
{
digitalWrite
(ledPin
, HIGH
)
;
// turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay
(
<1000
)
;
// wait for a second
digitalWrite
(ledPin
, LOW
)
;
// turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay
(
<1000
)
;
// wait for a second
}
In this code, we’re controlling an LED connected to GPIO 23.
const int ledPin = 23;
So, connect an LED to your ESP32 by following the next schematic diagram.
Important: always check the pinout for your specific board before building any circuit.
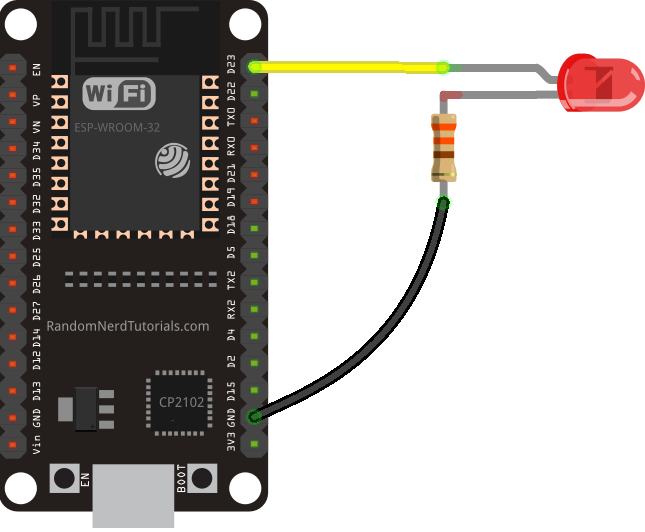
Here’s a list of the parts you need to build this previous circuit:
Plug your ESP32 development board to your computer and follow these next instructions:
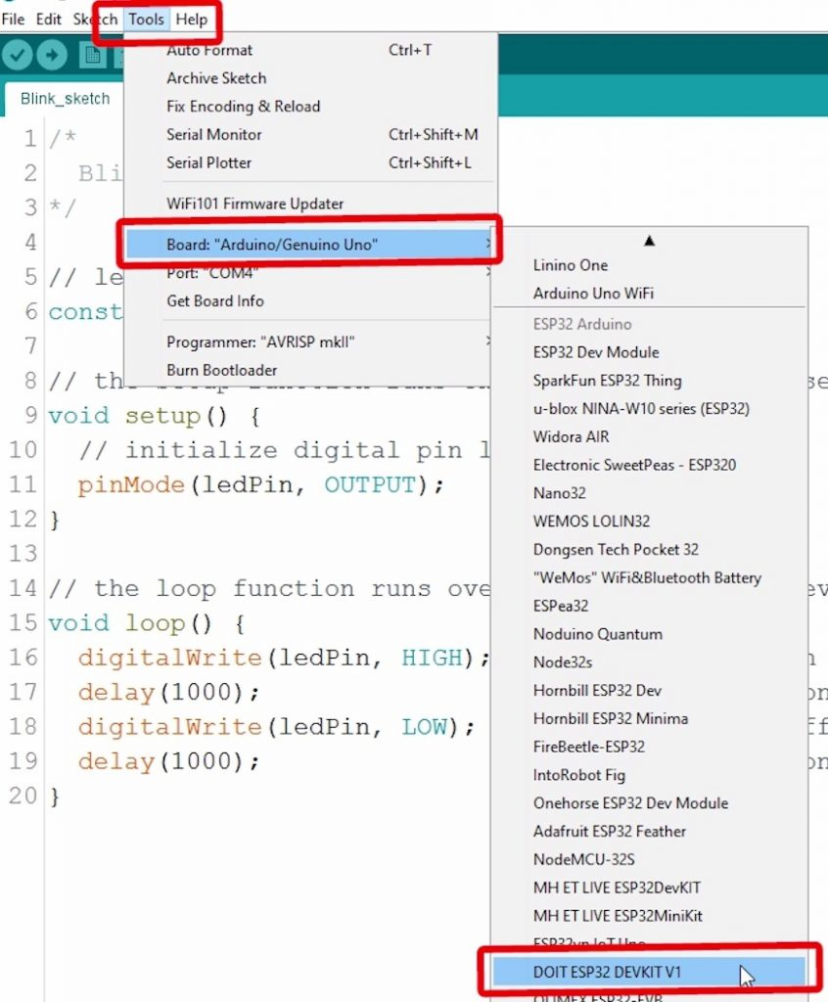
1) Go to Tools > Board , scroll down to the ESP32 section and select the name of your ESP32 board. In my case, it’s the DOIT ESP32 DEVKIT V1 board.
2) Go to Tools > Port and select a COM port available.
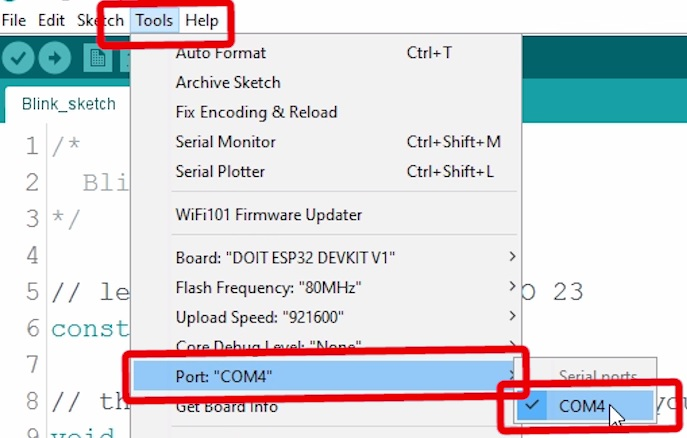
That’s it!
Note: If you get the following error when trying to upload code, it means that your ESP32 is not in flashing/uploading mode.
Failed to connect to ESP32: Timed out... Connecting...
To upload code, you need to follow the next steps (make sure you have the right board selected:
- Hold-down the “ BOOT ” button in your ESP32 board
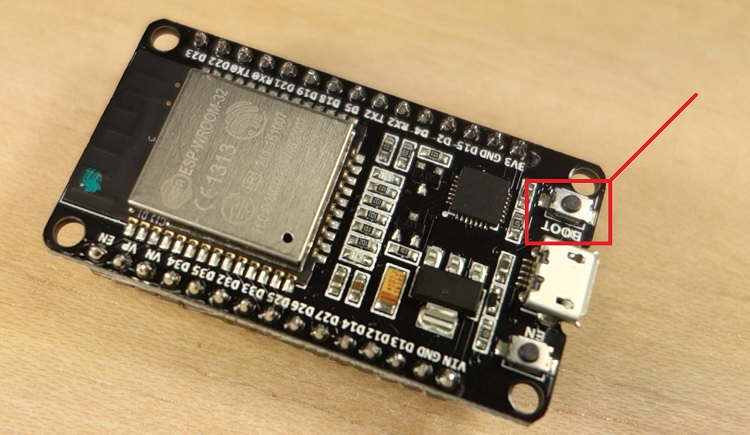
- After you see the “ Connecting….” message in your Arduino IDE, release the finger from the “ BOOT ” button:
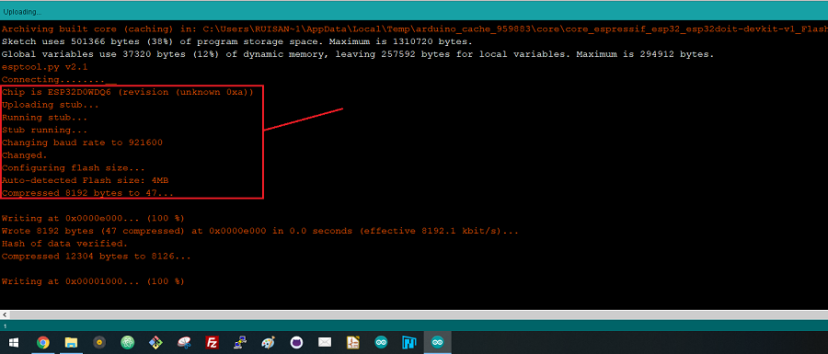
- After that, you should see the “ Done uploading ” message.
That’s it. After uploading the new sketch, you can press the “ ENABLE ” button to restart the ESP32 and run the new uploaded sketch.
Note: Learn how to fix the “Failed to connect to ESP32: Timed out waiting for packet header” error permanently when trying to upload new code to your ESP32 board once for all.
Demonstration
After uploading the code, the LED connected to GPIO 23 should be blinking every other second.
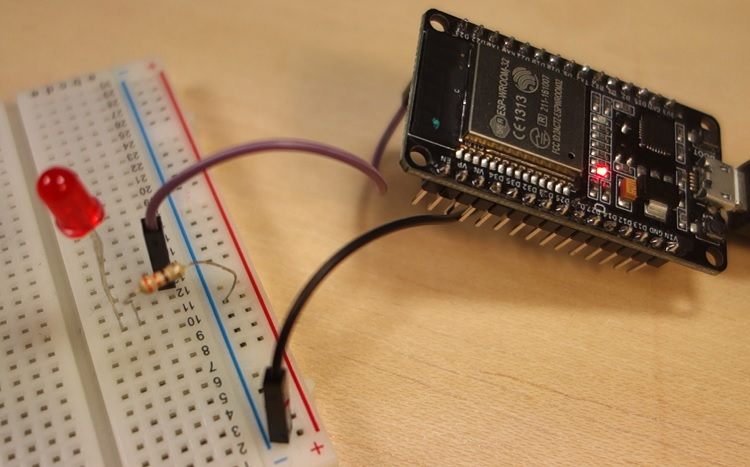
Wrapping up
We hope you’ve found this getting started guide useful. The blinking LED is just a simple project to get you started with the ESP32. This is also a great way to learn the procedure you need to do to upload code to your board.
If you like ESP32, we have more than 20 projects with the ESP32 you can find in our repository of ESP32 projects:
You may also like:
- ESP32 Pinout Reference: Which GPIO pins should you use?
- ESP32 Web Server Tutorial
- Learn ESP32 with Arduino IDE
- ESP32 vs ESP8266 – Pros and Cons
- Best ESP32 Development Boards
If you like ESP32 make sure you subscribe to our blog , so you don’t miss upcoming projects.
Do you have any questions? Leave a comment down below!
Thanks for reading,
P.S. If you like the ESP32, you might also enjoy our ESP32 course: Learn ESP32 with Arduino IDE


Build Web Server projects with the ESP32 and ESP8266 boards to control outputs and monitor sensors remotely. Learn HTML, CSS, JavaScript and client-server communication protocols DOWNLOAD »
Recommended Resources

Build a Home Automation System from Scratch » With Raspberry Pi, ESP8266, Arduino, and Node-RED.

Home Automation using ESP8266 eBook and video course » Build IoT and home automation projects.
Arduino Step-by-Step Projects » Build 25 Arduino projects with our course, even with no prior experience!
What to Read Next…
ESP32/ESP8266 MicroPython Web Server – Control Outputs
MicroPython: Program ESP32/ESP8266 using Mu Editor
ESP32 Digital Inputs and Digital Outputs (Arduino IDE)
Enjoyed this project? Stay updated by subscribing our newsletter!
70 thoughts on “Getting Started with the ESP32 Development Board”
Esp8266/esp32+usb camera stream to webpage is possible?
Learn ESP32
Protocols
Web Servers
DIY Cloud
ESP-NOW
Firebase
Modules
Sensors
Displays
ESP32 Features
Useful Guides
Other Projects
ESP32 Boards
Learn More

Visit Maker Advisor – Tools and Gear for makers, hobbyists and DIYers »
Home Automation using ESP8266 eBook and video course »
Build IoT and home automation projects.

Build Web Servers with ESP32 and ESP8266 »
boards to control outputs and monitor sensors remotely.